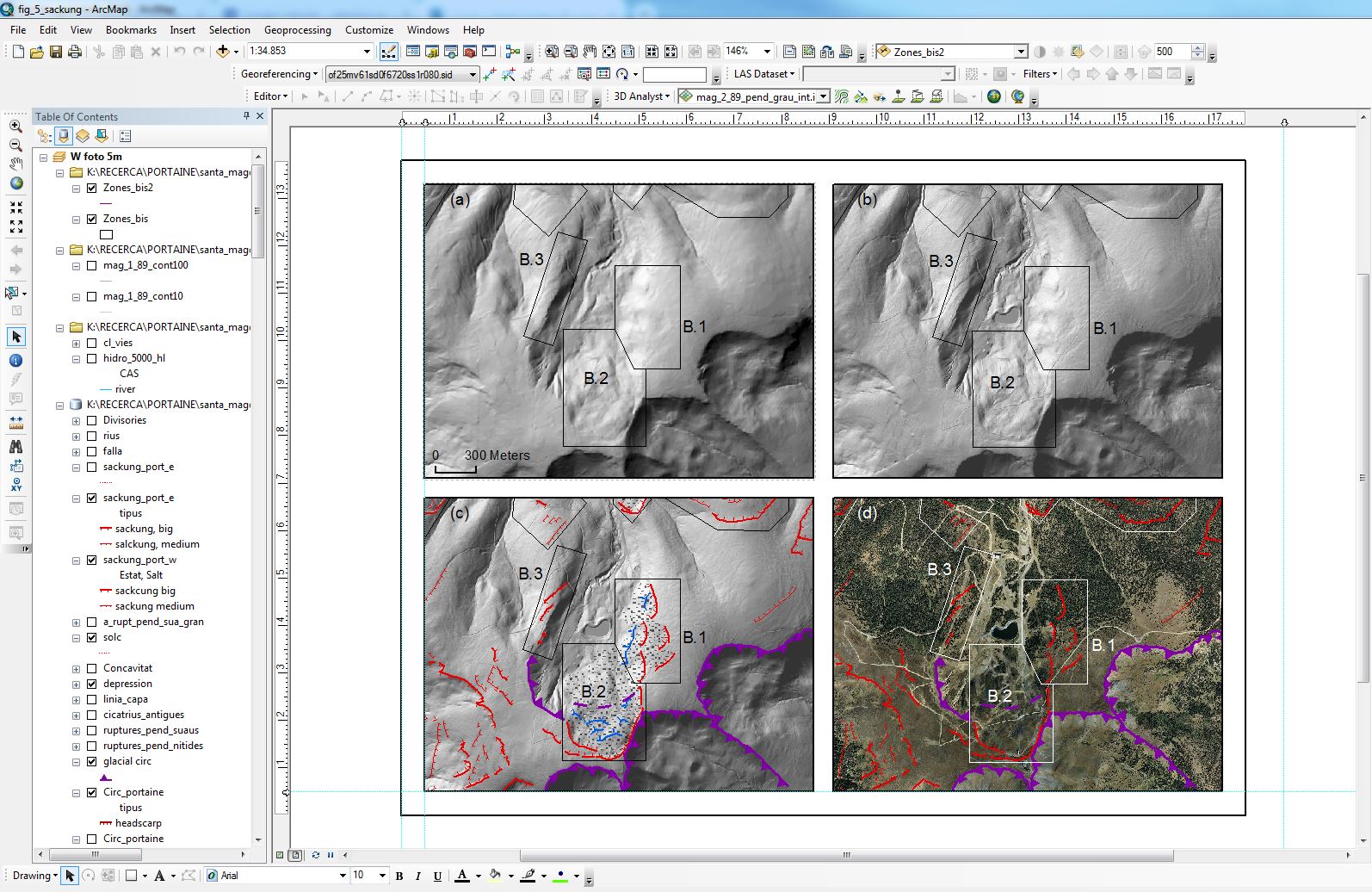
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are used for mapping and to help manage and analyse geographic data by using geodatabases and specific tools. We apply GIS for geomorphological analyses at different scales using the highest resolution datasets available in each study area (aerial and satellite images and High-Resolution Digital Terrain Models-HRDTM from airborne LiDAR data) together with field work. The analysis of LiDAR-based point clouds and HRDTM enables the detection of landforms otherwise indiscernible with aerial or satellite images because: 1) it furnishes a homogeneous overview of landforms across wide areas, which is a direct advantage over field mapping; 2) it permits the analysis of the bare earth surface below the canopy of forested terrains; and 3) it allows us to detect small changes on the Earth surface that would be difficult to detect by photogrammetry. These techniques are crucial to improve the detection of areas affected by geological processes in an efficient and reliable way.
Thematic mapping and hazard zoningxcom2023-07-30T14:05:44+02:00
We apply GIS-based specific tools that allow us to extract information from geographical data, like indices Ksn and SL to detect river longitudinal profile anomalies. Different endogenous and exogenous processes account for knickpoint/knickzone (anomalies) formation and migration, such as active tectonics, landslides, meander cut offs, as well as variations in bedrock resistance to erosion (i.e. litho-structural changes) or sediment load. Identification and analysis of geomophic indices combined with other methods allows to indentify the mutual interplay between slope and fluvial processes.