Ismael Sánchez-Vera, José Saura-Esteller, Sonia Núñez-Vázquez, Ana M Cosialls, Ouldouz Ghashghaei, Rodolfo Lavilla, Gabriel Pons, Joan Gil, Daniel Iglesias-Serret
DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115860
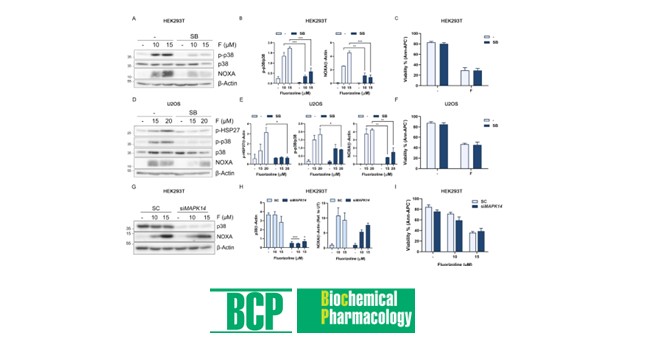
Fluorizoline is a prohibitin (PHB)-binding compound that induces apoptosis in several cancer cell lines as well as in primary cells from hematologic malignancies. In this study, we show that fluorizoline treatment triggers the activation of the stress-activated kinases c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 prior to caspase activation in human cell lines. However, the blockage of p38 and JNK activity with chemical inhibitors or siRNA-mediated downregulation of MAPK14 (p38) does not prevent fluorizoline-induced apoptosis, suggesting that the activation of these kinases plays an alternative role in the cell response to fluorizoline treatment. Here, we describe that fluorizoline treatment leads to the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin-8 (IL-8) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Importantly, we demonstrate that the activation of the stress-activated kinases JNK and p38 mediates the secretion of both IL-8 and IL-6. This study shows novel insights into the pro-inflammatory role exhibited by a compound that binds to PHB, thus supporting the potential of PHBs as anti-inflammatory proteins.